by | Nor Azliza Aris | Nur Suraya Mustafar | Wan Ahmad Jamaluddin W. Mohamad
To answer the question ‘does technology replace humanity’, we need to define the terms technology and humanity. Technology is defined as ‘the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes in general or specific areas’ (Oxford Dictionary), ‘branch of knowledge that deals with applied science, engineering, industry and etc. (Free Dictionary), and ‘Purposeful application of human activity (Business Dictionary); whilst humanity is defined as ‘characteristics that belong uniquely to human beings, such as kindness, mercy and sympathy (Yourdicionary.com), ‘the quality or state of being human’ (Merriam-Webster), ‘the state of being human’ (Oxford Dictionary), and ‘human qualities or characteristics, esp. those considered desirable’ ( Webster’s New World College Dictionary).
The next question is what or who is human? Dictionary .com defines human as ‘a human being, a person’, and Free Dictionary describes human as ‘member of genus Homo and especially of the species Homo sapiens’. That’s us.
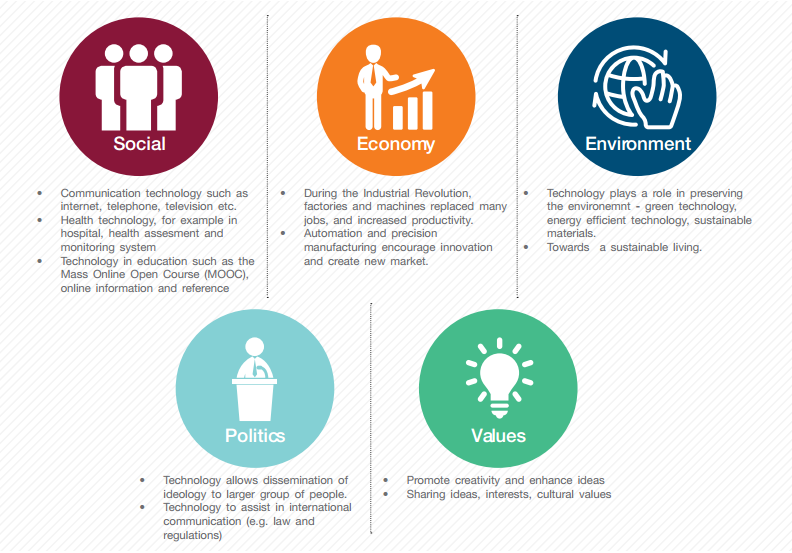
Looking at the definitions and the way we live our lives, we have to admit that technology plays major role in our daily life. Figure 1 shows how technology influence human in social communication, environmental care, economy and development, political importance and also in shaping the culture and values.
But, does technology replace humanity?
This article focusses on the influence of technology on the social aspect on human lives, especially communication.
Communication
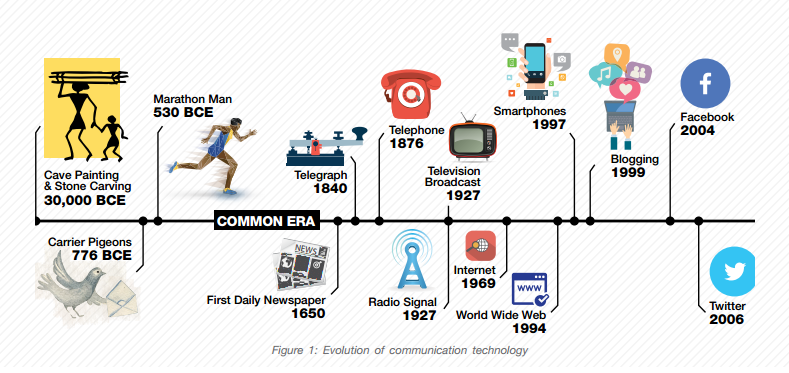
Communication is one of the most important aspects of human relationship. It is defined as the act or process of using words, sounds, signs, or behaviours to express or exchange information or to express your ideas, thoughts, feelings, etc., to someone else. Although face-to-face communication has almost remain unchanged – mostly through speeches and sign language, non-face-to-face communication – massages and long distance communication has evolved and developed tremendously, from the cave paintings and stone carvings of 30,000 BCE to carrier pigeons, marathon men and smoke signals before the Common Era, to telegraph, Morse code etc. of the 1700s and 1800s, and ICT of today. Figure 1 shows the evolution of communication technology since before the Common Era.
“Young parents are getting parenting advice through social media rather than seeking them from their parentsor grandparents. patients are known to seek medical counselling, and even medical prescriptions, without face-toface consultations with doctors or medical practitioners”
The evolution enabled people to communicate and connect to a much larger crowd in much shorter time. It took about 75 years for the telephone to connect 50 million people, while radio and television took 38 and 13 years respectively.
Today, the digital revolution have witnessed the Internet as the fastest growing instrument of communication in the history of civilization, and it may be the most rapidly disseminating tool of any kind ever. The convergence of information technology and the Internet may well become as transformative as the industrial revolution. ICT took only four years to reach an audience of 50 million people.
Information and communication technology (ICT) has changed the face of the world we live in. Defined as computers, software, telecoms (such as mobile and fixed phones), the Internet and satellite technologies, ICT enables people to communicate with family, friends and colleagues around the world instantaneously, gain access to global libraries, information and resources, and enumerable opportunities.
The introduction and development of social media enable people to connect creative and meaningful ways. A research by the Cooperative Research Centre for Young People, Technology and
Wellbeing (YAW-CRC) listed the benefits of social networking that includes:
1. supporting development of media literacy;
2. functioning as medium for education (e-learning, discussions, etc.);
3. generation of ‘original’ and ‘remixed’ creative content;
4. expression of individual and collective identity (similarity in interests and culture);
5. strengthening interpersonal relationships;
6. strengthening and building communities; and
7. civic engagement and political participation.
Social media also creates space for a new trend of advertising products and services, thus providing more effective marketing; enables faster and more effective dissemination of information; and provides a wider access to education.
REPLACING HUMANITY?
Is technology replacing humanity? To answer this question, we have to look at where and how human functions have been replaced through the utilisation of technology.
Seeking answers and solving problems
Today people are turning to their computers to look for answers, information and advice instead of seeking assistance of parents, family, peers or friends. Just turn on the ‘search engine’ and key in your question and, more often than not, you will get your answer almost immediately.
Young parents are getting parenting advice through social media rather than seeking them from their parents or grandparents. Patients are known to seek medical counselling, and even medical prescriptions, without face-to-face consultations with doctors or medical practitioners. Even school children need not turn to teachers or parents to help them with their school work. The recently release of ‘Slader’ and ‘Homework Helper’ apps have the function to solve mathematic equation. Students can get their answer by uploading the image of the question. However, these apps have been criticized as they may lead students to ‘cheat’ in examination.
Lost your way or do not know how to get to a certain destination? You don’t need to consult a policeman or approach the people you meet along the way to ask for direction. Just turn on your GPS, or even a simple Google search, and you’ll be guided all the way. And you’ll even get information on real-time traffic condition, speed traps, police road blocks, tolled routes, and be advised on the best route to take.
Exchanging ideas
The days that people need to meet up to chit chat and exchange ideas are things of the past. Face- to-face communication is slowly losing its importance. Today people can use the social media to chat up with almost anybody from any part of the world. Even some important meetings and conferences between government and/or corporate leaders are not conducted in meeting/conference rooms, but by tele-conferencing. ‘Friend’ today no longer means somebody that one have met or known personally, but could be anyone that one ‘meet’ or ‘contact’ through the social media.
Buying and selling
It is very rare to see door-to-door salesperson now as almost everything – from baby diapers to air tickets – could be purchased on line. Online advertisements offer potential customers a wide range of products and services for selection. Customers do not need to meet sellers to buy whatever they want.
THE NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF ICT
Despite all the beauty and advantages that communication technology brings, there are also the negative side of it.
Losing Creativity
Over reliance on technology to do the thinking – finding answers and solving problems – would affect one’s cognitive skills and limit creativity. A study by the Stanford University proves that technology can sometimes cloud our sensory judgement as we see only factual and textual information instead of an array of human emotions. Turning to devices make all decisions erodes the ability to make critical decision.
A study by University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) shows that communication technology also contribute to the decrease of sensitivity to emotional cues — losing the ability to understand the emotions of other people. The displacement of in-person social interaction by screen interaction is reducing social skills.
…communication technology also contribute to the decrease of sensitivity to emotional cues
Less Interaction
The desire to find meaningful connections leads people to become more focused on sharing with their social network friends in real-time on line that they neglect to realize how they are isolating themselves from the people they are actually with. Michael J. Bugeja, a professor of communications at Iowa State University and author of Interpersonal Divide: The Search for Community in a Technological Age said that the practise of texting in the presence of others, once considered as rude but common today, makes people lonelier than ever.
The trend to pay more attention to on line friends in the presence of others is effecting Malaysian youth. A report by the Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) in 2013 showed that the mobile phone is seen as the most important tool in a young person’s life.
About 36.8% of respondents consider the mobile phone the most important media tool, followed by computer or laptop (29.5%) and the Internet (13.2%). Another report indicated that one-third of all time spent online in Malaysia is on social networking websites. Facebook and Twitter ranked as the top two preferred social networking sites in 2011, with 10.17 million and 1.43 million total unique visitors respectively. There were more than 12 million Facebook users in 2011. In 2013, there were about 1.3 million Twitter users in Malaysia. A Yahoo!-Synovate 2011 study which interviewed 2,635
Peninsular Malaysians found that 90 percent used social networking sites — an increase of 61 percent from 2010.

Cyber Warfare
ICT has opened up the possibility for cyber warfare – to conduct attacks on the strategic or tactical resources for the purpose of espionage or sabotage by nation-state or international organization. The use of network technologies and the exploitation of cyberspace for intelligence and attack has become a normal part of military activity. Cyber warfare would involve disruption of crucial network services and data, damage to critical infrastructure, and the creation of uncertainty and doubt among opposing commanders and political leaders.
Cyber-attack provides an ability to strike both tactical and strategic targets from a distance, using inexpensive systems. Cyberattacks are unlikely to be decisive and will not by themselves produce victory, particularly against a large and powerful opponent. But they do offer strategic advantage and will be part of future military conflict.
Cybercrime
Cyber-crimes are committed virtually through the Internet online. Among the most common cybercrimes are theft, fraud, harassment, pornography, and 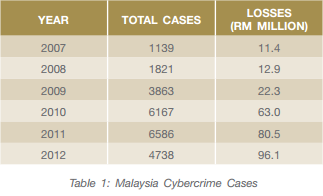 stalking.
stalking.
The Royal Malaysia Police stated that top three reported cases are in E-commerce fraud in online purchase, parcel scam, VOIP scam by cross border syndicates. In 2013, a total of 389 cyberbullying reports were lodged by Internet users to the Cyber999 Help Centre, a 55.6% increase from 250 in 2012. A study by CyberSecurity found that 13% of the 1,255 respondents admitted being victims of cyber-bullying while 26% or 2,509 confessed they had once been bullied online.
Exposure to new subculture
Subculture is defined as a cultural group within a larger culture, often having beliefs or interests at variance with those of the larger culture. Subcultures are not manufactured entities. They are formed by a diversity of individuals who share some similar consciousness by participating in a specific event/activity (which makes them a subcomponent of a larger culture). In the study of criminology and sociology, subculture is defined as subnormal, dysfunctional, delinquent, resistant, and consumerist. Subcultural group is also defined in terms of ‘their potential menace to social and racial welfare, the subcultural defectives forms the crux of this problem’.
Although subcultures did exist before the middle of 20th century, they are generally smaller and mostly limited within ethnic and racial groups that share the language, food, and customs of their heritage. For example, a ‘Zoot Suit’ outfit that was popular among Mexican American and African Americans youths in the 1940s. It was a distinctive part of the ‘Pachuco’ culture – as a way for the youth of minority groups to express their individuality and opposition towards the establishment.
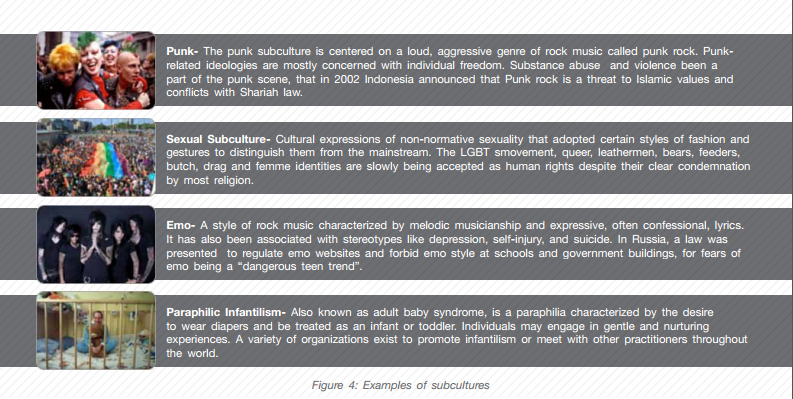
The explosion of subcultures in the second half of the 20th century has a lot to do with the development of communication and transportation infrastructures (and market capitalism’s push to render humans into consumers). Subculture thrives with the advancement of personal computers and the internet. Websites like Tumblr, Reddit and 4chan became the playing ground for different communities all around the world to receive and share information about different cultural forms. Figure 3 shows some of the subcultures that was popular in the 20th century. It is without doubt that technology is slowly but surely replacing humanity. But, why should it be? Technology is invented and created by human, and it should not be allowed to erode human’s function.
REFERENCES
- http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/communication
- United Nations Cyberschoolbus, http://www.un.org/cyberschoolbus/briefing/technology/tech.pdf
- Collin, P., Rahilly, K., Richardson, I. &Third, A. (2011) The Benefits of Social Networking Services: A literature review. Cooperative Research Centre for Young People, Technology and Wellbeing. Melbourne. http://www.uws.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0003/476337/The-Benefitsof-Social-Networking-Services.pdf
- Is Technology Making Us Less Human?, 2012, http://spark.qualcomm.com/salon/technology-making-us-less-human
- Is technology making us less human? http://www.techradar.com/news/world-oftech/future-tech/is-technology-making-usless-human–1171002
- Media Matters: Networked Media Content Research Report by Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission, http://www.skmm.gov.my/skmmgovmy/media/General/pdf/Media-Matters_-Research-Report.pdf
- Mapping Digital Media: Malaysia – A Report by the Open Society Foundations, http://www.opensocietyfoundations.org/sites/default/files/mapping-digital-mediamalaysia-20130617.pdf
- Uhls Y.T. et. al.,2014, Five days at outdoor education camp without screens improves preteen skills with nonverbal emotion cues, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0747563214003227
- How Does Cyber Warfare Work?, 2013, Forbes, http://www.forbes.com/sites/quora/2013/07/18/how-does-cyberwarfare-work/
- Thresholds for Cyberwar, James A. Lewis, Center for Strategic and International Studies, September 2010SIS
- Cybercrime : Malaysia, http://www.skmm.gov.my/skmmgovmy/media/General/pdf/DSP-Mahfuz-Majid-Cybercrime-Malaysia.pdf
- The Star: Cyber-bullying reports up 55.6% in 2013, http://www.thestar.com.my/News/Nation/2014/02/24/Cyberbullying-up-55pc/
- http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/us/definition/american_english/subculture
- Blackman, S. (2014).Deviant Behavior, Subculture Theory: An Historical and Contemporary Assessment of the Concept for Understanding Deviance
- Lewis, E. O. (1933). Types of Mental Deficiency and Their Social Significance.
- Blackman, S. (2014). Subculture Theory: An Historical and Contemporary Assessment of the Concept for Understanding Deviance. UK: Canterbury Christ Church University.
- Matusitz, J. (2007). The Implications of the Internet for Human Communication. Journal of Information Technology Impact (Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 21-34)
- Sullivan, J.L. (2013). Media Audiences: Effects, Users, Institutions, and Power. SAGE Publications, Inc.